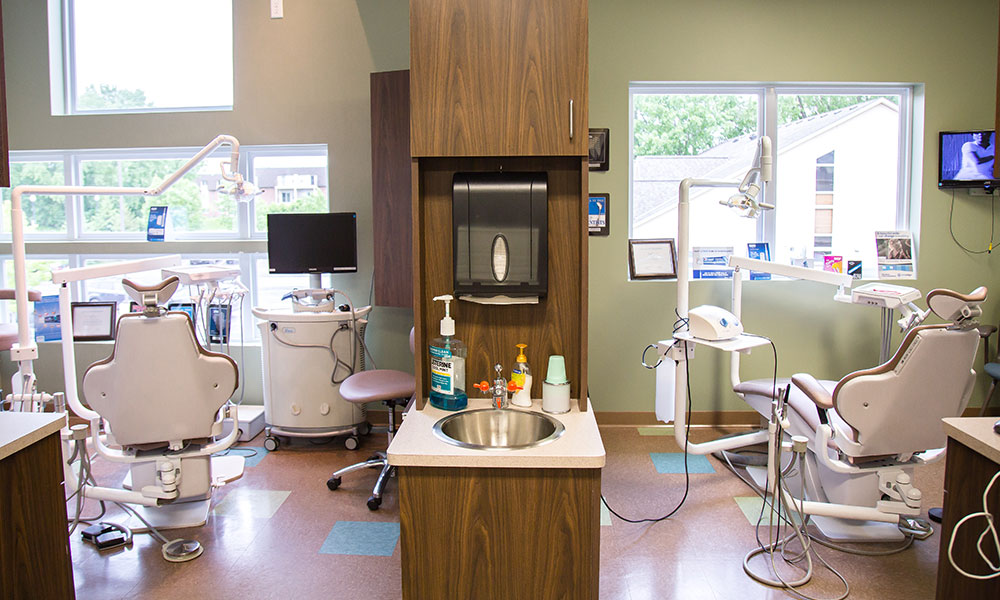
Dentistry is a complex but fascinating and rewarding career which is why so many dentists choose to go it alone eventually by starting their own practice. While it’s an exciting prospect, there is also a huge amount to think about and organise to give the practice the best chance of success. One of the major considerations has to be that when you are setting up a new dental practice, you need to ensure you have all of your tools and equipment in place from day one. In this guide you will find all the essential equipment you need to start your own dental practice.
Examination tools
· The dental examination mirror or mouth mirror not only enhances visibility of the patient’s mouth by reflecting light onto particular areas but also acts as a separator during examinations.
· A probe is a long thin instrument used in examinations but there are a few different types depending on the shape of the tip: periodontal, sickle and briault.
· Dental retractors enable the dentist to move the cheeks, tongue and lips so they are not obstructing a procedure.
Treatment tools
· A dental drill is a handheld drill which works at high speeds to remove decay and reshape teeth before a crown or filling is inserted.
· Dental burs are handpieces which are usually made of very strong material like diamond or tungsten carbide for cutting. There are several types and sizes for a wide range of different procedures.
· An excavator is a double headed instrument which removes dentine from teeth.
· A syringe may be required to administer a numbing agent which will prevent the patient from feeling pain during a procedure.
· Tweezers are ideal for removing and placing items in the mouth, e.g. cotton wool.
· A curette is a small hand tool with a rounded tip available in different shapes and sizes for removing subgingival calculus.
· A burnisher smooths and/or polishes composite fillings, emphasises grooves in the teeth and removes excess filling material from the tooth’s surface.
· Chisels (sometimes called Coupland’s elevators) are used during extractions and are available in sets of 3.
· Osteotomes can cut, compress or otherwise reshape bone to improve the fit of dental implants.
Rotary tools
Rotary instruments, as the name suggests, are connected to hoses and rotate at different speeds with a dental bur on the end. Examples include:
· Turbines
· Dental Micromotors
· Micromotor Straight Hand Pieces
· Contra Angle Hand Pieces.
Light Curing Dental Lamps
A dental curing light speeds up the process of curing or hardening adhesives, sealants and composites through a UV light. Curing lights are available with halogen or LED bulbs.
Large machinery
· An autoclave can sterilise tools with 100ºC steam.
· An X-ray machine is crucial in dentistry for diagnosing and treating dental issues.
Furniture
· You will need a cabinet lamp (floor or wall-mounted) with an articulated head and arm to enable you to work accurately and comfortably. The lamp will help you identify colours with precision while treating patients.
· An ergonomically designed medical stool will enable you to work without causing strain or injury to your body.
· The dental chair is where your patient reclines during treatment and as such should be comfortable and supportive. Some dental chairs include a dental unit which can store a range of tools and pieces of equipment.