Introduction
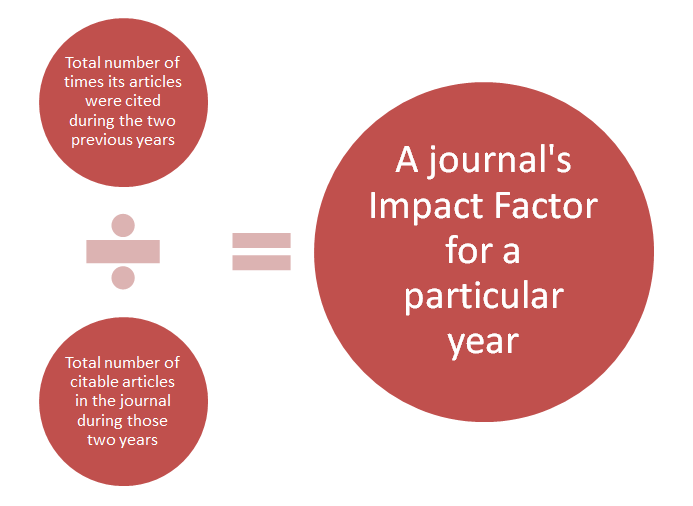
Impact Factor (IF) is a measure of the average number of citations of a journal article in a specific year. It is used to find the importance or ranking of a magazine by counting the number of cited articles. The calculation is based on a two-year period and includes the number of citations divided by the number of citations. Therefore, journals with big impact driven are generally considered more prestigious than journals with less effect. It is important to understand that impact radius do not find the effect of single articles, but rather the collection of magazines.
Tool for measuring journal impact
citation reports
SC Imago journal ranking
Standardization impact of the source of each paper
• Citation reports
Scopus Cite Score measures the citation effectiveness of a particular magazine. It is completely free to use, transparent and calculates indicators based on Scopus data. It has more than 24,000 ranking titles and covers more than 300 disciplines. With Cite Score Tracker, you can monitor the performance of specific journals throughout the year.
The main purpose of citation analysis is to count the number of times other people mention a particular article in their publication. This analysis includes citation counting to measure the effect of journals, specific authors, or publicity. However, there is no single tool that can capture all broadcast and their citations to today. Therefore, if you want to conduct a thorough citation analysis of writers or publications, you need to search multiple databases. Some of the most common citation analysis resources include Web of Science and Google Scholars Finally, Google Scholar has the most journals and publication types in all disciplines. This is because, unlike Scopus it indexes non older sources. Google Scholar all provide citation digits for the essay they index.
• SC Imago journal ranking
SC Imago is a portal to collect data from the Scopus database. It does not provide citation counts at the article level, but provides different data at the journal level, such as the journal’s first index and SC imago’s own journal rankings. Ranking lists of journals appear in various scientific fields. A certain quartile of this list-Q1, Q2, Q3, or Q4-is a parameter frequently used by journals.
• Source standardization impact of each paper
The source standardization impact (SNIP) of each paper measures context sensitive citation effects by weighting citations based on the total number of citations in the topic. In areas that are unlikely to be cited the impact of a single citation is rated higher, and vice versa.
Compared with well-known journal impact factors, SNIP corrects the differences in citation practices between scientific fields, so that the citation effects between various disciplines can be compared more accurately.
Altmetrics
Altmetrics measures the quality and quantity of attention that scientific papers receive on social media and through citations and article downloads. It is a non-historical type of indicator that supplements traditional indicators with additional figure.
Its reliability
The most well-known newspaper metric is the Journal’s impact factor used by the science website. The calculation of the magazine’s impact factor covers a great time. It is a proportion of two whole numbers. First, how many times have the articles have been mentioned, published in this twelfth period in a magazine, they were quoted in the following year. Therefore, this number is divided by the number of boxes published at that time of the twelfth period. There is ongoing debate related to the reliability of the magazine’s impact factor. A diary with a big impact rate can contain a unique object that mentioned thousands of times and ten articles that have been mentioned only a couple of times.
Conclusion
I hope you have got a clear idea about the journal impact factors.