Gamification seems to be the buzz word used to describe a way for organizations to improve their adoption and engagement strategy, but what does it mean? Gamification in its purest form as defined on Wikipedia; typically, gamification applies to non-game applications and processes, to encourage people to adopt them or to influence how they are used. Gamification works by:
Gamification seems to be the buzz word used to describe a way for organizations to improve their adoption and engagement strategy, but what does it mean? Gamification in its purest form as defined on Wikipedia; ‘typically, gamification applies to non-game applications and processes, to encourage people to adopt them or to influence how they are used’.
Gamification works by:
o making technology more engaging
o encouraging users to engage in desired behaviors
o showing a path to mastery and autonomy
o helping to solve problems and not being a distraction
o taking advantage of humans’ psychological predisposition to engage in gaming
Gamification is part of your daily interactions, such as collecting points to get discounts on food or clothing or gaining points to achieve frequent flyer status as an example of a gamified strategy deployed by organizations to engage and increase loyalty to a product or service by users.
Let’s take a brief look at gamification framework, satisfying behaviors, and driving behaviors using a gamification program approach.
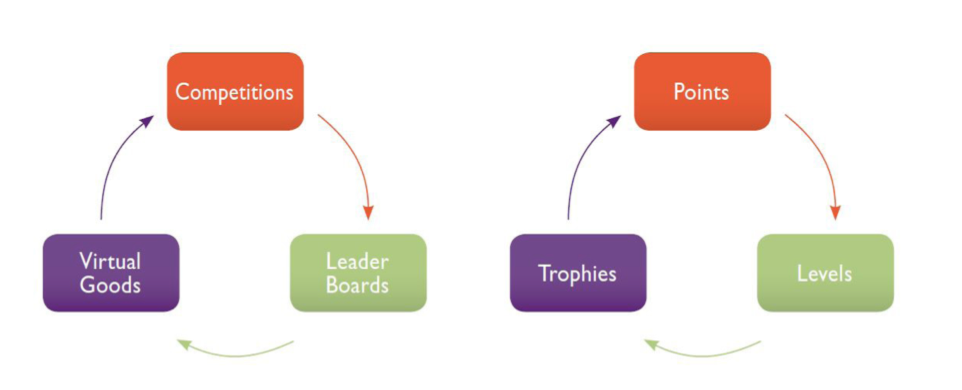
Gamification Framework
The primary purpose of gamification is to change the behaviors of users of a product or service in a spirited and fun way. As illustrated below, gamification is a continuous feedback loop, which allows for real-time improvement.
1. Points are generated by users of the gamified environment.
2. Levels are used to segment the users by participation in the gamified environment.
3. Virtual goods are organizational SWAG used to reward participants.
4. The leaderboard is generated from the points earned by users.
5. Virtual trophies are used to identify and recognize achievement.
6. Competition among users is what drives the gamified environment.
Satisfying Behaviors
Gamification appeals to the most fundamental instincts in people. In that, it appeals to our intrinsic reward system. When you join an airline frequent flyer program for example, you can earn a particular status level. These types of earning points challenges appeals to the intrinsic reward area of our brains.
Why? Because, when we earn points with program participation, we gain status and that status, is recognized by the airline. Then the airline provides some symbol to acknowledge your loyalty such as a bag tag with your status (Silver, Gold, Platinum) that others identify you as a frequent flyer and that status makes you feel good.
Gamification Behavior Impact
An intrinsic reward system is something that individuals are motivated by oneself to work towards something they value and something meaningful. People have the need and desire to achieve a task, work, or goals to satisfy this driving need.
Gamification helps fill the intrinsic reward system of individuals, which is a primary benefit of gamification in your workplace environment.
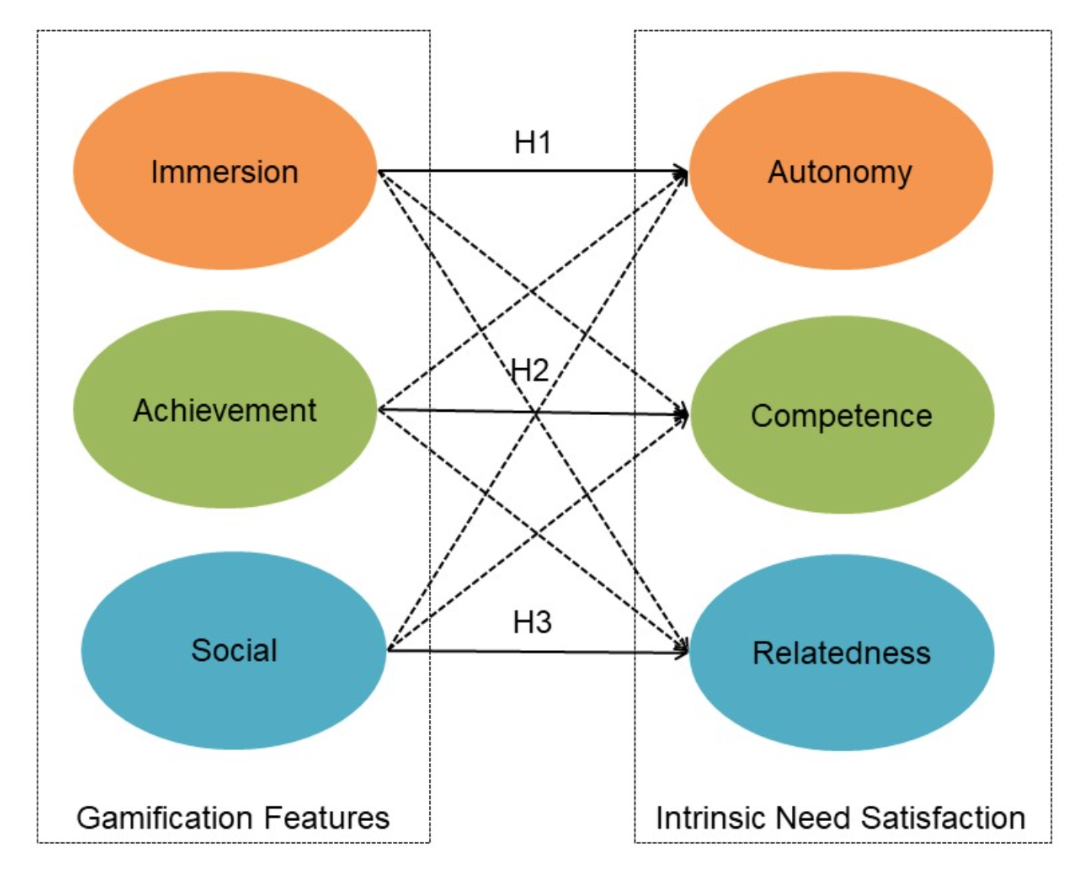
In a study below conducted by Xi, N., & Hamari, J. (2019), they indicate a positive relationship between two specific elements, gamification features, and intrinsic need satisfaction. The study indicated the following results:
Positivity associated with autonomy and game features.
Positivity and satisfaction with achievement features indicated the strongest relationship with autonomy and competence need satisfaction.
Positivity associated with the social gamification features along with competence, autonomy and relatedness satisfaction.
In summary, the study postulates that a gamification environment can have a positive effect on an individual’s intrinsic need satisfaction.
Gamification to Drive User Adoption and User Engagement
Microsoft pioneered the use of badges with the introduction of the Xbox system in 2002, which is now a standard feature of a gamification program. The use of badges drove the retention of users, which was a critical driver of getting users to return back to the platform time and time again.
Returning to the platform drove increased levels of adoption and engagement by users globally. This same principle applies to drive adoption of training, learning, skill enhancement, and other organizational programs and activities for users.
Ways Gamification Drives User Adoption and Engagement
Achievement Recognition
Provide a badge to recognize the achievement for the completion of various activities such as a completed profile, or update status. The more tasks you finish using the new tools, the more badges you achieve and can motivate users to keep and stay engaged. Make recognition appealing to individuals and teams. People like to achieve things and be recognized for that achievement.
Virtual Re-engagement
Create a mechanism in the gamification program that requires users to complete a time-bound requirement as part of the life cycle of the gamified approach. Example, you have to update your profile every 30 days, or you will lose points for inactivity on your account as a way to keep people coming back. The feedback loop can help provide what needs to be done to improve the tool as part of continuous user improvement.
Users Engagement
Establishing challenging activities as part of the gamified environment is what people want and you should use to drive behaviors. It doesn’t have to be Fortnight or Candy Crush (addictive games), but the idea is to make the gamified program exciting and consuming.
Community Platform
Gamification is about generating social engagement. All you have to do is to look at the number of virtual platforms that drive a sense of community such as Xbox, PlayStation, The Sims, and other multiple game platforms that drive a competitive environment for all users as a tool to learn, improve skills, and collaborate with others.
Create Program Curiosity
To help increase the adoption and engagement of your program, ensure things are curious and mix things up using for example; an online pop quiz to help drive more engagement or a one-question survey as another way to engage users.
Conclusion
Gamification can be a robust tool for those individuals charged with driving adoption and engagement in the organization. Those change leaders must understand the pros and cons of using a gamification program.
The financial cost and loss of employee productivity can be high if the program you implement hasn’t been fully vetted using your organizations use cases for success.
Gamification can be a powerful tool to help change behaviors, drive engagement, and increase adoption activities for users in your organization. It requires commitment and perseverance to deliver a program that is suited for your organizational culture.
Sources
Xi, N., & Hamari, J. (2019).Does gamification satisfy needs? A study on the relationship between gamification features and intrinsic need satisfaction. International Journal of Information Management, 46, 210–221.
“Using Gamification to Engage Employees”. Bunchball, 2016. www.bunchball.com
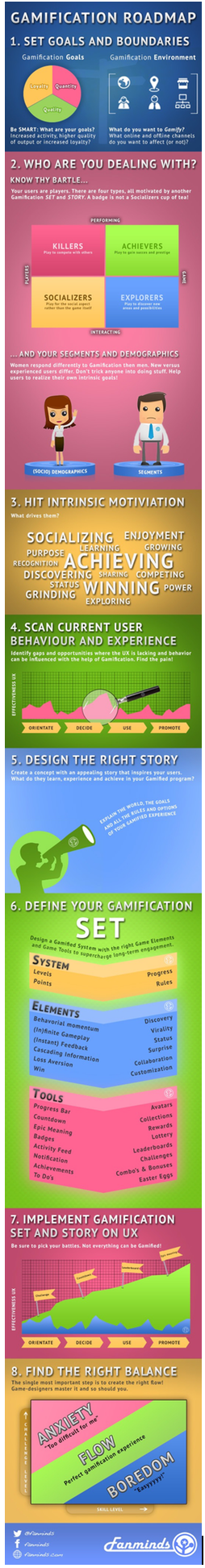
https://elearninginfographics.com/the-gamification-roadmap-infographic/
Example of how to Create a Gamification Program